Outlet Plug Type F, Outlets, Voltage, Plug Type F, CEE 7/4 German 16 A/250 V, Schuko
Type F Power Outlet
Type F Plug Adapter and power Outlet description
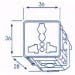
The Type F plugs have two round, parallel prongs and it’s also equip with 2 recesses one on the top, and one on the bottom that are used to receive the 2 metal plates located on the Type F power outlet for grounding. This style of grounding it’s know as “Schuko” style
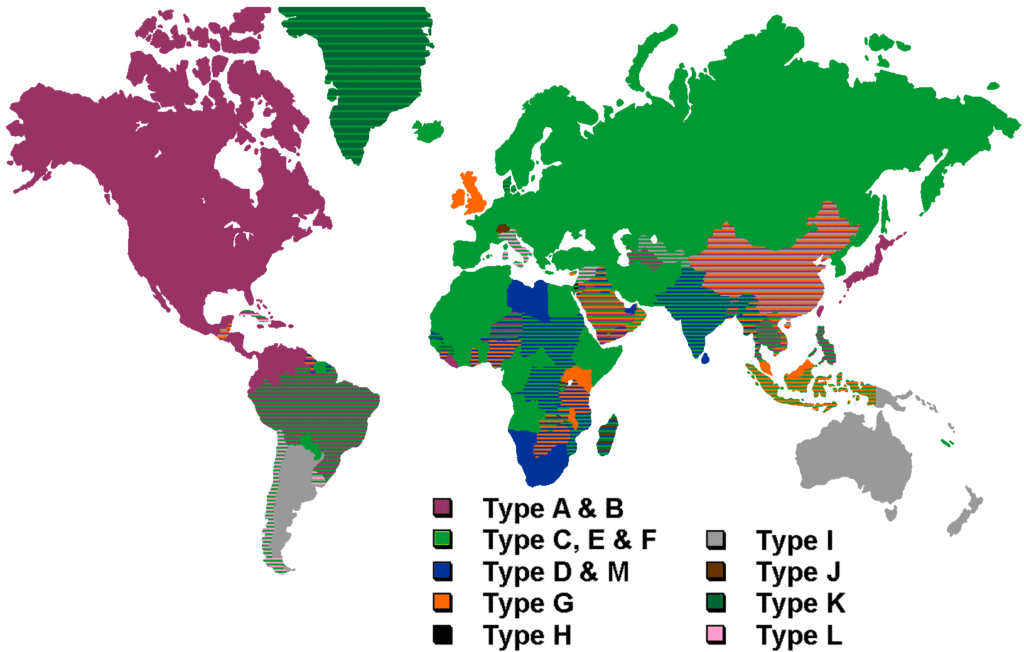
Countries that Use plug adapter type F
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, American Samoa, Andorra, Armenia, Aruba, Austria, Azerbaijan, Azores, Belarus, Bhutan, Bosnia, Bulgaria, Cape Verde, Chad, Croatia, Cuba, East Timor, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Guinea, Hungary, Iceland, Indonesia, Italy, Jordan, Korea, Laos, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Madeira, Monaco, Montenegro, Mozambique, Myanmar, Netherlands, Netherlands Antilles, New Caledonia, Niger, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, Suriname, Sweden, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uruguay
 Type F Plugs and plug adapters
Type F Plugs and plug adapters
- The Type F plugs are found in some European countries such as Germany and Austria.
- Type F plugs have 2 round, parallel pins and 2 openingd on the top and bottom designed for grounding contact with the power receptacle type F.
- The grounding for type F plugs it’s commonly know as Shuko style.
- Most type F plug adapters contain grounding receptacle for Type E and F outlets as noted below, for more versatility when travelling through multiple countries.
- Type F plugs and adapters may also be used in type C outlets with no eath grounding.
Plug Adapters for Type F French 2-pin Plug 16 A / 250 v
Type F Power Outlet
- Type F power outlets posses 2 round parallel inserts located 19mm apart, and a metal pin placed at the top of the receptacle that connects to the metal plate located on the plug for grounding.
- Type E outlets are used in countries such as Poland, France and Denmark.
- type E wall outlets may also be suited for type C plugs
UNIVERSAL Outlets for Type F (NO GROUNDING)
Type F Power cords
- Allows the plug-in of equipments into a Type F wall outlet
- Rated for 16A 220-250 Volts 50/60HZ can be used on Computers and other items that contain detachable power cords.
- Note : Power cords are an alternative for plug adapters, and do not convert electricity.
Outlets, Plugs, Power cord, and Extension cords for Type F
TYPE F plugs and outlets
(These plugs and outlets will be found in : Germany,Austria,Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Portugal,and other European countries)

Type F plugs also know as Schuko style plugs or CEE 7/4 (16 Amps/250 Volts grounded) it’s made of two parallel round inserts and metal slits on the top and bottom, (Schuko grounding) that receive the grounding plates when connected to type F power outlets.With the exception of the grounding style,type E,F and C plugs are very similar.So, in order to facilitate traveling between countries that use these style plugs, most Type F plug adapters are designed with grounding receptacles and inserts for both type F,and Type E sockets (called CEE 7/7 plug), examples of these plugs adapters the are EuropeanShucko and Univ-9Shucko plugs
Have you ever looked at a Type F plug and wondered what those two round, parallel prongs and two recesses were all about? Well, wonder no more! In this guide, we will demystify the Type F plug and explain the power behind those prongs.
The Type F plug, also known as the Schuko plug, is a common electrical plug used in many European countries. It is easily recognizable by its two round, parallel prongs and two recesses, one on the top and one on the bottom. These recesses are used to receive the two metal plates located on the Type F power outlet for grounding.
But why is grounding important? Grounding is a safety feature that helps protect you from electrical shocks. When an electrical device is properly grounded, any excess electrical current is safely redirected into the ground, preventing it from flowing through your body. This is especially important in situations where there is a fault in the electrical system or a surge of electricity.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the prongs. The two round, parallel prongs are designed to fit snugly into the corresponding holes in the power outlet. This ensures a secure connection and allows electricity to flow from the outlet to your device.
But what about those recesses? As mentioned earlier, the recesses are used for grounding. The two metal plates located on the Type F power outlet make contact with the recesses on the plug, completing the grounding circuit. This helps to protect you from electrical shocks and ensures the safe operation of your electrical devices.
It’s worth noting that the Type F plug is not only used in Europe but also in other parts of the world, including some countries in Africa, Asia, and South America. So, if you’re planning to travel internationally or purchase electrical devices from abroad, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the Type F plug.
In conclusion, the Type F plug may look a bit different from what you’re used to, but it serves an important purpose. Its two round, parallel prongs and recesses are designed to ensure a secure connection and provide grounding for your electrical devices. So, the next time you encounter a Type F plug, you’ll know the power behind those prongs!
Other countries that use type F outlets and plugs are :Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, American Samoa, Andorra, Armenia, Aruba, Austria, Azerbaijan, Azores, Belarus, Bhutan, Bosnia, Bulgaria, Cape Verde, Chad, Croatia, Cuba, East Timor, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Guinea, Hungary, Iceland, Indonesia, Italy, Jordan, Korea, Laos, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Madeira, Monaco, Montenegro, Mozambique, Myanmar, Netherlands, Netherlands Antilles, New Caledonia, Niger, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, Suriname, Sweden, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uruguay
FAQs:
Rules of Thumb for Appliance Voltage Compatibility
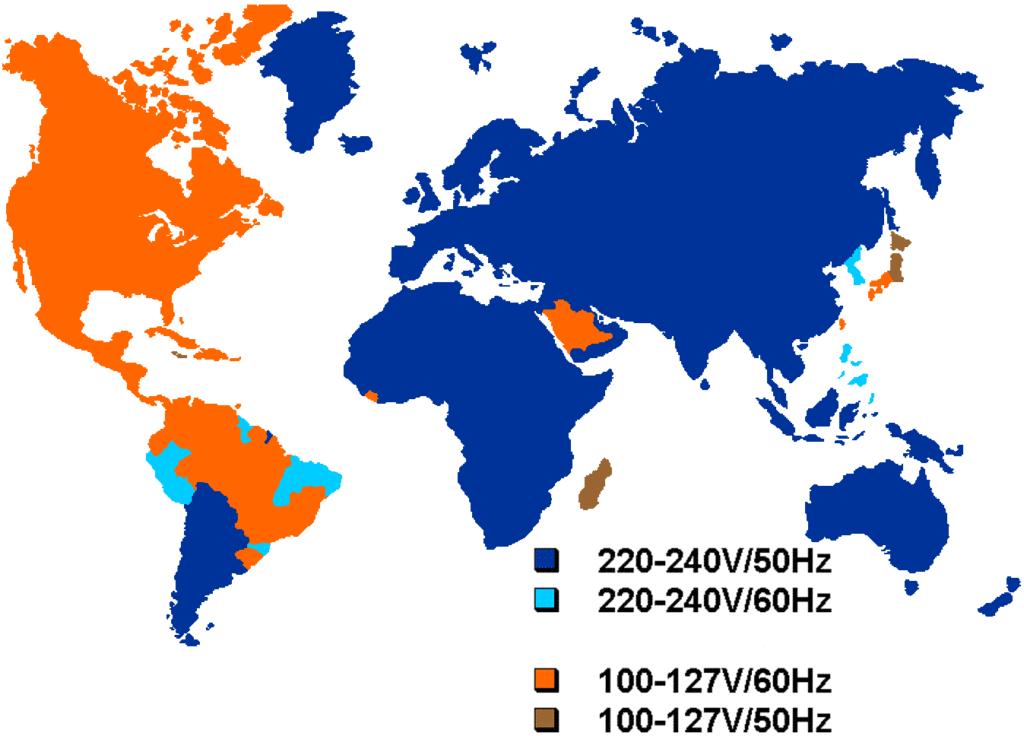
It’s important to understand that there’s no such thing as a “standard” electrical input/output for electrical appliances. The information below is just a general guideline, and it may or may not be correct for your specific brand and model. The only way to know for your specific appliance is to check.
Laptop computer: Usually 100-240V, 50/60Hz, auto-switching. A travel plug adapter works just fine all by itself.
Desktop computer: Usually switchable between 110-120V and 220-240V via a small switch on the back of the computer, near the cooling fan. A travel plug adapter will work fine as long as the voltage switch is set to the proper position.
Cell phone: Usually comes with a charger that is 100-240V compatible, but that is by no means always the case. It’s very important to check the charger. If it says “100-240V” then a plug adapter will work fine. If not, the easiest solution is probably to contact your cell phone provider and buy a new charger which is multi-voltage compatible, and attach the appropriate plug adapter to the multi-voltage charger.
PDA/Blackberry/etc: Almost always comes with a charger that is 100-240V compatible. Simply attach a plug adapter to the charger’s plug.
Digital camera: Chargers are usually 100-240V compatible. A plug adapter is usually sufficient.
Hair dryer/curling iron/flat iron/etc: Most U.S. and Canadian hair care appliances are only compatible with 110-120V, though some higher-end models can be switched between voltages. If your brand/model has a voltage switch, then a plug adapter is sufficient. Otherwise, the appliance will require that the voltage be changed. Since hair dryers and other hair care appliances usually don’t contain any electronic circuits, a voltage converter is usually more convenient than a step-down transformer.
Electric shaver: Most U.S. and Canadian corded electric shavers are only compatible with 110-120V. Cordless/rechargeable shavers often come with chargers that are 100-240V compatible.
CPAP Machine: 50/50 shot, there’s no telling. A lot of CPAP machines are built with DC motors because they’re quieter. DC motors plug into AC power sources, of course, through an AC adapter. Since AC adapters are converting an AC voltage to a smaller DC voltage anyway, the AC input voltage is often irrelevant. If the AC adapter says “100-240V” then a plug adapter will work just fine. But this is by no means true of all CPAP machines. Some brands/models use AC motors and are only compatible with 110-120V. If that’s true of yours, then theoretically a voltage transformer + a plug adapter would at least allow it to power up. But in practice, the difference in frequency (Hz) may negatively affect the machine’s performance. For most appliances, the effect is negligible. But for a CPAP machine, we’ve been told that the effect can be significant. The better solution may be to just buy a multi-voltage compatible CPAP machine, rather than to depend on a transformer.
iPod: You’ll have to check the iPod’s charger. There are so many different versions, it’s impossible to keep up with what kind of charger ships with any particular model. If the iPod’s charger says “100-240V” then a plug adapter is sufficient. Otherwise, if it says “120V” then you’ll need a voltage transformer. Or you’ll need to replace the iPod’s charger with one that is 100-240V compatible.
Audio/Video Equipment, including Televisions, Stereo Components, VCRs, DVD Players, Video game consoles (X-Box, Wii, Playstation, etc.): Most equipment of this type is purposely manufactured to be localized to a particular country or geographic region. It’s all part of the “war on piracy” and for the most part, it’s not worth the trouble to bring this kind of item abroad. Even if you want to fight the battle of getting power to the device, there will probably be compatibility/standards issues related to the audio/video signals, scan rates, etc. These are beyond the scope of our business, and we don’t claim to be authorities on those matters. Television broadcast standards are different (NTSC vs. PAL), audio broadcast standards are different, CD and DVD media are usually “region-locked” to a particular geographic area (i.e. European DVDs/game discs won’t play on most North American DVD players/game consoles) and a host of other issues beyond simply getting power to the device. If you’re dead set on bringing A/V equipment to another country, you’ll want to consult an A/V specialist.
Power Tools: Most U.S. and Canadian power tools are built for 110-120 volts, and will require a step-down voltage transformer as well as a plug adapter. However, some cordless/rechargeable power tools ship with chargers which are 100-240V compatible. Check your charger. If it says “100-240V” then a plug adapter is sufficient.
Air conditioners, refrigerators: Appliances which contain a compressor require a special type of transformer called a “3-tap transformer” because in order for the compressor to function properly, the output voltage supplied by the transformer needs to be slightly adjusted up or down to compensate for the difference in frequency (Hz.)
Clothes dryers and Electric ranges: North American clothes dryers and ranges usually connect to a specialized 2-phase household electrical circuit. You’ll want to consult an electrician.
Using Appliances Abroad:
What do I need to use my appliances abroad ?
Plug Adapters
They do not convert electricity. They simply allow a dual-voltage appliance, a transformer or a converter from one country to be plugged into the wall outlet of another country. The plug of a Continental European appliance will not fit into an outlet in a foreign country without an adapter.
Converters
Converters and transformers both step up or down the voltage, but there is a difference in use between them. Converters should be used only with “electric” products. Electric products are simple heating devices or have mechanical motors. Examples are hair dryers, steam irons, shavers, toothbrushes or small fans. Converters are not designed for “continuous duty” and should only be used for short periods of time (1 to 2 hours). Additionally, most converters can only be used for ungrounded appliances (2 pins on the plug). Converters must be unplugged from the wall when not in use.
Transformers
Transformers also step up or down the voltage, but they are more expensive than converters and are used with “electronic” products. Electronic products have a chip or circuit. Examples are radios, CD or DVD players, shavers, camcorder battery rechargers, computers, computer printers, fax machines, televisions and answering machines. Transformers can also be used with electric appliances and may be operated continually for many days. The advantage of converters, however, is that they are lighter and less expensive.
Computers are electronic devices and therefore they must be used with a transformer, unless they are dual voltage. Fortunately, most laptop battery chargers and AC adapters are dual voltage, so they can be used with only a plug adapter for the country you will be visiting.
Transformers are sold in various sizes based on how much wattage they can support. Therefore one must pay careful attention to the wattage ratings of the appliances to be plugged into a transformer. The wattage rating of the transformer must always be larger than the wattage rating of the appliance to be plugged into it (plus a 25% buffer to allow for heat build-up in the transformer or converter). When plugging multiple items into a power strip, then into the transformer, you must calculate the combined wattage of all appliances and the power strip, then add an additional 25% to that total.
The appliance’s voltage and wattage requirements are listed on the manufacturer’s label located on the back or at the bottom of the appliance. In some cases, the voltage and amperage will be listed, but not the wattage. If this is the case, simply multiply the voltage by the amperage rating to find the wattage rating (e.g. 230 V * 1 A = 230 W).
Below is a list that gives an idea what the wattage of common appliances is. Use this as a guide only. Always check your appliance first !
- 75 watts: small, low-wattage appliances such as radios, CD players, heating pads, and some televisions.
- 300 watts: larger radios, stereo consoles, electric blankets, sewing machines, hand mixers, small fans and most TV sets.
- 500 watts: refrigerators, hair dryers, stand mixers, blenders and some stereo equipment.
- 750 watts: projectors, some sewing machines and small electric broom type vacuums.
- 1000 watts: washing machines, small heaters, some coffee makers and vacuums.
- 1600 – 2000 watts: dishwashers, most appliances that have heating elements such as toasters, electric deep-frying pans, irons, and grills.
- 3000 watts: heaters and air conditioners.
Transformers and converters only convert the voltage, not the frequency. The difference in cycles may cause the motor in a 50 Hz appliance to operate slightly faster when used on 60 Hz electricity. This cycle difference will cause electric clocks and timing circuits to keep incorrect time: European alarm clocks will run faster on 60 Hz electricity and American clocks will lose some 10 minutes every hour when used in Europe. However, most modern electronic equipment like battery chargers, computers, printers, stereos, DVD players, etc. are usually not affected by the difference in cycles and adjust themselves accordingly the slower cycles.

 Type F Plugs and plug adapters
Type F Plugs and plug adapters